
Select the best single answer for each question:
1. Use the thermochemical equation
2HF(g) ![]() H2(g) + F2(g) , DH
= 542.2 kJ
H2(g) + F2(g) , DH
= 542.2 kJ
to determine the enthalpy of formation of HF(g).
| A) | -542.2 kJ | |
| B) | -271.2 kJ | |
| C) | -135.6 kJ | |
| D) | 135.6 kJ | |
| E) | 271.2 kJ | |
2. The number of ions released when 0.618 mol of copper(II) nitrate trihydrate dissolves completely in water is
| A) | 1.12 ´ 1024 | |
| B) | 1.49 ´ 1024 | |
| C) | 7.44 ´ 1023 | |
| D) | 1.20 ´ 1024 | |
| E) | 2.23 ´ 1024 | |
3. Which is the weakest electrolyte in water?
| A) | HNO3 | |
| B) | H2SO4 | |
| C) | NaOH | |
| D) | HCl | |
| E) | CH3COOH | |
4. List
the spectator ions for the reaction KI(aq)
+ AgNO3(aq) ![]() KNO3(aq) + AgI(s)
KNO3(aq) + AgI(s)
| A) | K+, I-, Ag+, NO3- | |
| B) | Ag+, I- | |
| C) | NO3- | |
| D) | K+, NO3- | |
| E) | K+ | |
5. What is the concentration of an HCl solution if 45.6mL of it neutralizes 26.3mL of 0.165M NaOH ?
| A) | 9.52 ´ 10-2 M | |
| B) | 1.23 ´ 10-1 M | |
| C) | 2.92 ´ 10-1 M | |
| D) | 7.16 ´ 10-2 M | |
| E) | 1.90 ´ 10-1 M | |
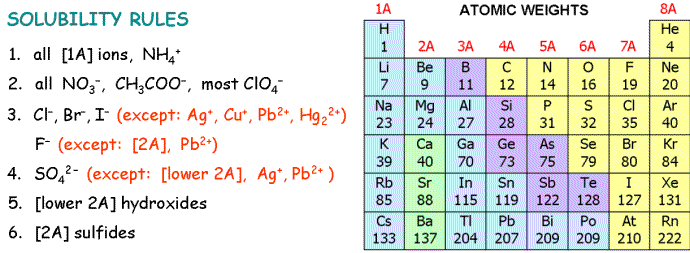
6. Which mixture of solutions does not produce a solid precipitate?
| A) | silver(I) nitrate and sodium chloride | |
| B) | copper(II) sulfate and potassium carbonate | |
| C) | calcium nitrate and sodium sulfide | |
| D) | potassium iodide and lead(II) nitrate | |
| E) | sodium hydroxide and cobalt(II) chloride | |
7. What is DE for a thermodynamic system that absorbs 200 cal of heat from the surroundings while delivering 100 cal of work?
| A) | 300 cal | |
| B) | 100 cal | |
| C) | 0 | |
| D) | -300 cal | |
| E) | -100 cal | |
8.
How
much heat (J) increases the temperature of 1430 kg of iron from 250°C to 800°C?
The specific heat capacity of iron is 0.450 J/g-°C.
| A) | 9.94 ´ 107 J | |
| B) | 5.15 ´ 108 J | |
| C) | 7.87 ´ 108 J | |
| D) | 3.54 ´ 108 J | |
| E) | 5.20 ´ 107 J | |
9. The oxidation number of sulfur in SO2 is
A) 7 B) 4 C) 6 D) 3 E) 5
10. The oxidation number of tellurium in H2TeO4·2H2O is
A) 7 B) 4 C) 6 D) 3 E) 5
11. The oxidation number of chlorine in ClO4- is
A) 7 B) 4 C) 6 D) 3 E) 5
12. The oxidation number of vanadium in H2V4O11 is
A) 7
B) 4
C) 6
D) 3
E) 5
13.
The zinc ion in the reaction Cu(s)
+ Zn2+(aq) ![]() Cu2+(aq) + Zn(s)
Cu2+(aq) + Zn(s)
| A) | is a spectator ion | |
| B) | undergoes oxidation | |
| C) | undergoes reduction | |
| D) | none of the above | |
14. Identify the oxidizing agent in the reaction
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2
H+(aq) + 2 HSO4-
(aq) ![]() 2 PbSO4(s) + 2 H2O(l)
2 PbSO4(s) + 2 H2O(l)
| A) | Pb | |
| B) | H+ | |
| C) | PbSO4 | |
| D) | PbO2 | |
| E) | HSO4- | |
15.
A chemical reaction at constant pressure transfers 200 kJ of heat to the
surroundings.
The enthalpy change of the reaction is best
described as:
| A) | DH = 200 kJ (endothermic) | |
| B) | DH = -200 kJ (exothermic) | |
| C) | DH = -200 kJ (endothermic) | |
| D) | DH = 200 kJ (exothermic) | |
| E) | none of the above | |
16.
Use the reaction 3 C(s)
+ 4 H2(g) ![]() C3H8(g),
DH
= -104 kJ to determine DH
for
C3H8(g),
DH
= -104 kJ to determine DH
for
0.5 C3H8(g)
![]() 1.5 C(s) + 2 H2(g),
DH
= ?
1.5 C(s) + 2 H2(g),
DH
= ?
| A) | 52 kJ | |
| B) | -208 kJ | |
| C) | 104 kJ | |
| D) | -52 kJ | |
| E) | 208 kJ | |
17.
Classify the reaction: H2SO4(aq)
+ Ba(OH)2(aq) ![]() 2H2O(l) + BaSO4(s)
2H2O(l) + BaSO4(s)
| A) | oxidation-reduction | |
| B) | acid-base neutralization | |
| C) | precipitate formation | |
| D) | acid-base neutralization and precipitate formation | |
| E) | acid-base neutralization and oxidation-reduction | |
18. Use the heats of formation to find DH° for the reaction
8 NH3(g) + 6 NO2(g) ![]() 7 N2(g) + 12 H2O(g)
7 N2(g) + 12 H2O(g)
|
DH°f |
||||||
| A) |
-2734 kJ |
N2(g) | 0 kJ | |||
| B) | -3074 kJ | NH3(g) | -46 kJ | |||
| C) | -3470 kJ | NO2(g) | 33 kJ | |||
| D) | -3470 kJ | H2O(g) | -242 kJ | |||
| E) | -3129 kJ | |||||
19. Find the moles of electrons transferred in the oxidation-reduction reaction
8
NH3(g)
+ 6 NO2(g)
![]() 7 N2(g) +
12 H2O(g)
7 N2(g) +
12 H2O(g)
|
This type of problem will NOT be covered on the exam. |
||
| A) | 12 | |
| B) | 36 | |
| C) | 18 | |
| D) | 30 | |
| E) | 24 | |
20. How many mL of 1.25 M H2SO4 solution react with 2.77g of aluminum hydroxide by
3
H2SO4
+ 2
Al(OH)3
![]() 6 H2O
+ Al2(SO4)3
6 H2O
+ Al2(SO4)3
| A) | 36.5 mL | |||
| B) | 18.9 mL | |||
| C) | 42.6 mL | |||
| D) | 28.4 mL | |||
| E) | 53.3 mL | |||
![]()